In this presentation, General Surgeon Dr. Wong Kwong Hieng looks at what is breast cancer, the types of breast cancer and treatment available at Timberland Medical Centre.
Breast Cancer by Dr. Wong Kwong Hieng (General Surgeon)
What is breast cancer?
- The breast is an organ that consists of milk producing glands and ducts, connective tissue and fat.
- Breast tissue consists of lobules, ducts and nipple. Analogy that of tree trunk, major roots and branching smaller roots.
- Breast cancer develops from cells lining of the lobules and draining ducts (not the fat and connective tissue)
- Most breast cancers are invasive ductal carcinoma that spread to the axillary lymph nodes and distant organs (lungs, liver and brain)
- Staging depends on the extent of spread
Types of Breast Cancer
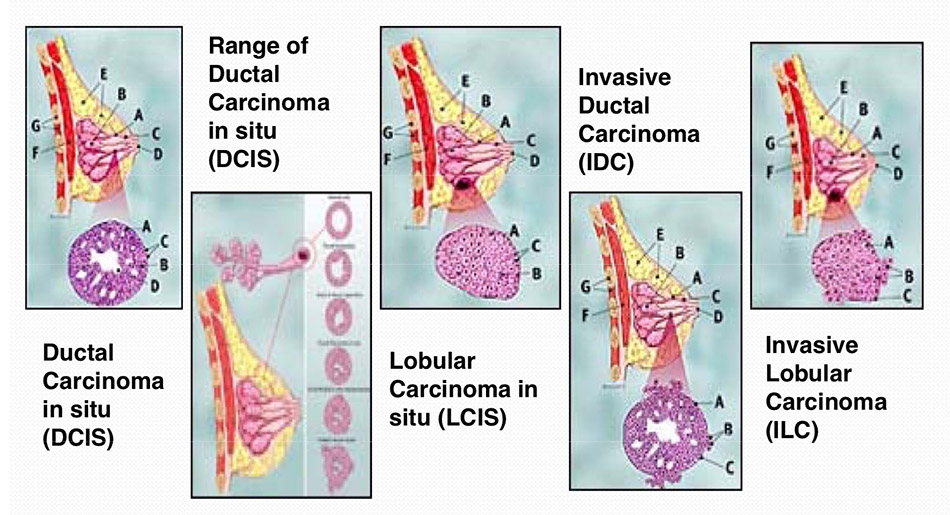
Non-Invasive and Invasive DCIS and LCIS
- Ductal Carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
- Range of Ductal Carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
- Lobular Carcinoma in situ (LCIS)
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC)
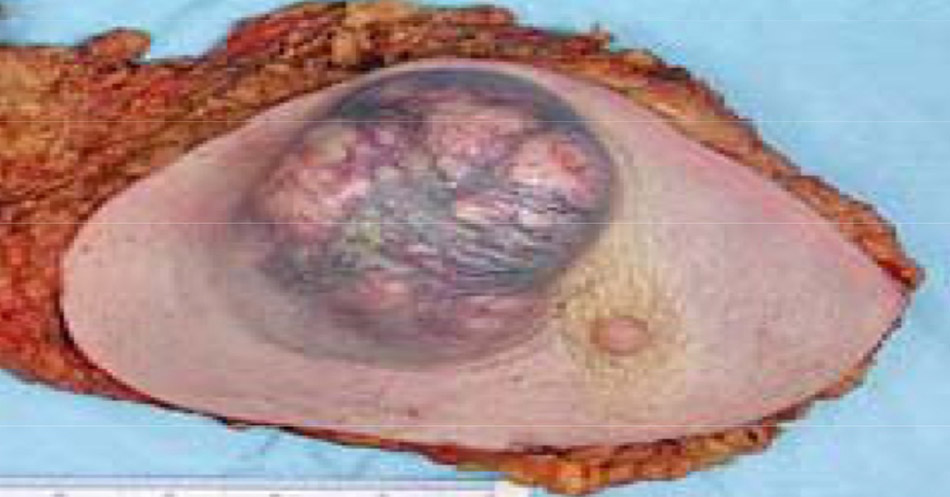
Typical macroscopic (gross) appearance of the cut surface of a mastectomy specimen containing a cancer (in this case, an invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast, pale area at the center).

Mastectomy specimen containing a very large cancer of the breast (in this case, an invasive ductal carcinoma).
How common is breast cancer?
- Commonest cancer in women worldwide (one million a year)
- Second most common cancer after lung cancer (both sexes combined)
- In UK 44,000 new cases each year diagnosed (30% of all female cancers, 1/8 women affected during their life)
- Highest incidence in USA and Europe
- Developing world is catching up
- Age incidence lowering
Does breast cancer occur in men?
- Less Than 1% of all breast cancers
- In UK about 300 cases per year (ratio: 1:140)
- Easier to diagnose
- Spread Faster
- Behaviours and treatment same as women cancer

What are the risk factors?
>> Age
- Incidence increases with age
- More aggressive in younger woman
>> Geographical Variation
- White females more than double the risk of Asian women but this is changing
>> Reproductive Factors
- Early menarche
- Late menopause
- Age at first pregnancy
- Number of children
- Breast feeding
>> Inherited Risks
- 10% due to inherited factor
- BRCA1, BRCA2
>> Previous Breast Disease
- Lumps and previous operation / biopsy
>> Dietary
- High fat intake
- Alcohol
- Exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke
- obesity
>> Radiation Exposure
>> Pills and Hormone Replacement Therapy
>> Exercise
What are the symptoms and signs of breast cancer?
- Painless lump
- Skin changes
- Nipple discharge
- Signs of spread
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
- Self examination (screening)
- Physical examination
- Mammograms
- Ultrasound Scanning
- MRI
- Needle Biopsy (FNAC)
- Open Biopsy
Pictures of self-exam


How is breast cancer treated?
Depending on Staging…
- Early operable breast cancer
- Locally advanced breast cancer
- Advanced breast cancer
Treatment Options:
- Surgery
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Hormonal therapy
Pictures of treatment

Lumpectomy
Showing: Jill – Lumpectomy, Maggie – needle directed biopsy/lumpectomy

Mastectomy
Showing: Skin – Sparing Mastectomy, Modified Radical Mastectomy, Total (Simple) Mastectomy, Radical Mastectomy, Vicki – Mastectomy
Estrogen Receptors
Showing: Tamoxifen Blocking Estrogen Receptors, Biopsy: Margins of Resection, Port for Chemotherapy
Radiation Treatment

Showing: Front View, Side View, Cross-sectional view
Pre-surgery preparation
What about laboratory tests (blood and tissue tests) for breast cancer
Health Screening from local labs often be misleading:
- Tumour marker (CA15.3)
- Gene markers (BRACA 1& 2)
- Oetrogen / Progesterone receptors
- Herceptin 2 gene mutation

How is the outlook of breast cancer treatment?
Depends on staging, tumour type and grade, hormonal status, genetic abnormality and age
What about breast cancer support group?
- Counselling
- Double blows to women: ‘I am going to die from cancer’ and psychological trauma of loosing a breast especially in younger women.
- Prophylactive mastectomies
- Plastic surgery for breast reconstruction following mastectomy

SBCSG – Sarawak Breast Cancer Support Group
“We Support”
TEL: 082-411 137
Address:
Matahari
Lorong 2 Maxwell
Jalan Maxwell
Jalan Tun Abg. Hj. Openg
93000 Kuching
Sarawak







